If you’re new to the world of cannabis, you might encounter terms like “indica,” “sativa,” and “hybrid” when discussing different types of marijuana. Here’s a guide to help you understand these categories, their unique characteristics, and their historical background.
Types of Cannabis Strains
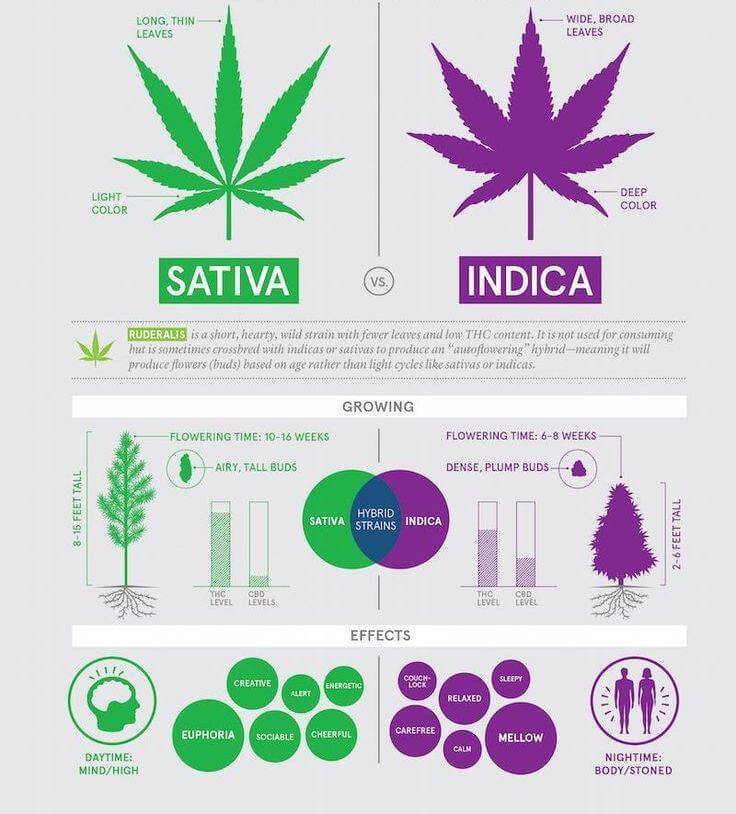
1. Indica Cannabis
Characteristics:
Indica plants are typically short and bushy with broad, wide leaves. They tend to grow shorter and thicker compared to sativa plants. Indica strains are known for their relaxing and sedative effects, often leading to a couch-lock feeling. This makes them ideal for evening use or before bedtime.
Medical Uses:
Indica strains are commonly used to alleviate symptoms of chronic pain, insomnia, muscle spasms, and anxiety. They can also be beneficial for individuals with conditions such as multiple sclerosis, sleep apnea, arthritis, and Parkinson’s disease.
Appearance:
Indica buds are generally dense and compact. The plant’s thick foliage can sometimes result in lower yields compared to sativas.
2. Sativa Cannabis
Characteristics:
Sativa plants are typically taller and leaner than indica plants, sometimes reaching heights of up to 20 feet. They feature narrow leaves and have a more open, airy structure. Sativas are known for their uplifting and energizing effects, making them suitable for daytime use.
Medical Uses:
Sativa strains are often chosen to combat fatigue, depression, and mood disorders. They can also be helpful for individuals dealing with chronic pain, headaches, or glaucoma. Sativas are preferred for their stimulating effects, which can enhance creativity and focus.
Appearance:
Sativa buds are usually lighter and more elongated than indica buds. The plant’s longer flowering period and warmer growing conditions often result in buds with hints of deep red or orange.
3. Hybrid Cannabis
Characteristics:
Hybrids are a blend of indica and sativa strains, aiming to combine the desirable traits of both. Depending on the hybrid’s lineage, it can offer a balanced experience, providing both a body high and a head high. This makes hybrids versatile and suitable for various occasions.
Medical Uses:
Hybrids can be tailored to address a wide range of medical conditions by balancing the effects of indica and sativa. They may be used to treat pain, inflammation, or mood disorders while also providing energy or relaxation based on the specific strain.
Appearance:
The appearance of hybrid buds can vary widely, reflecting the traits of its parent strains. Hybrids may exhibit characteristics of both indicas and sativas, leading to diverse bud shapes and effects.
History of Cannabis Species
Cannabis Sativa:
Cannabis sativa was the first cannabis species to be formally classified. Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus identified this strain in 1753, naming it “sativa,” derived from the Latin word for “cultivated.” Sativas originally thrived in equatorial regions such as Thailand and Colombia due to their preference for hot climates and ample sunlight.
Cannabis Indica:
In 1785, French naturalist Jean-Baptiste Lamarck discovered Cannabis indica, a new type of marijuana plant. Indica plants are shorter, with thicker branches and broad leaves. They are adapted to harsher environments and have a higher chlorophyll content, making them distinct from sativas. Indicas were originally found in regions like India and Turkey.
Cannabis Ruderalis:
Discovered by Russian botanist D.E. Janischevsky in 1924, Cannabis ruderalis is a less common strain characterized by its small size and lack of branching. Despite its low THC content and minimal medical use, ruderalis genes are now utilized to create autoflowering cannabis varieties. These plants are adapted to grow in harsh conditions and are often crossed with other strains to produce hybrids.
Identifying Cannabis Strains
Indica vs. Sativa:
- Indica: Short, bushy plants with dense, compact buds. Effects are relaxing and sedative. Buds are typically darker and more robust.
- Sativa: Tall, thin plants with elongated, airy buds. Effects are uplifting and energizing. Buds often have lighter hues with deep red or orange tints.
Hybrid Buds:
Hybrids can vary widely in appearance and effects, depending on their genetic makeup. They may display characteristics of both indicas and sativas, offering a versatile experience.
Identifying an Indica
Indica plants are typically shorter and more compact compared to sativas. Here are some key characteristics to help you identify an indica:
- Appearance: Indica plants are shorter and less spread out, resulting in denser and more compact buds. The buds tend to stay close to the stem’s nodes, making them appear fuller and harder to the touch.
- Buds: When examining indica buds, look for their thickness. Indica buds generally have a dense and solid structure, which can make them feel more substantial compared to sativa buds.
- Color: Indicas often grow in cooler climates and can exhibit shades of purple, especially towards the end of their flowering cycle.
Understanding Cannabis Strain Names
The name of a cannabis strain can sometimes give clues about its type, but it’s not always definitive. Generally, strains with names like “Haze” are sativas, while strains named “Kush” are typically indicas. However, with the constant breeding of new hybrids and creative naming by companies, strain names can be misleading.
Different companies may offer strains with the same name, but their characteristics can vary. The effects and traits of a strain can change based on growing conditions and the specific lineage of the plant. For example, two different breeders may produce their own versions of “Girl Scout Cookies,” which might differ in effects and appearance.
Effects on Health
It’s important to note that the effects of cannabis are not solely determined by whether a strain is indica or sativa. Instead, the impact of cannabis on health is influenced by its cannabinoid and terpene profiles.
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds in cannabis that interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in the human body. The ECS is a complex network of receptors located in various parts of the body, including the brain, organs, and cells. These receptors help regulate processes such as mood, pain, and inflammation.
As of now, scientists have identified over 110 cannabinoids, with estimates suggesting there could be over 200. Some of the most well-known cannabinoids include:
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol): The most famous cannabinoid, THC is primarily responsible for the psychoactive effects or “high” associated with cannabis. It can influence mood, appetite, and pain perception.
- CBD (Cannabidiol): CBD is gaining popularity for its therapeutic benefits without causing a “high.” It has been studied for its potential to alleviate anxiety, pain, and seizures.
- CBN (Cannabinol) and CBG (Cannabigerol): These cannabinoids are also significant. CBN is known for its sedative effects, while CBG may have potential benefits for pain and inflammation.
Understanding the cannabinoid profile of a strain can help in choosing the right one for your needs, whether you’re seeking relief from specific medical conditions or looking for a particular type of effect.

